4. Dihedral Group
-----
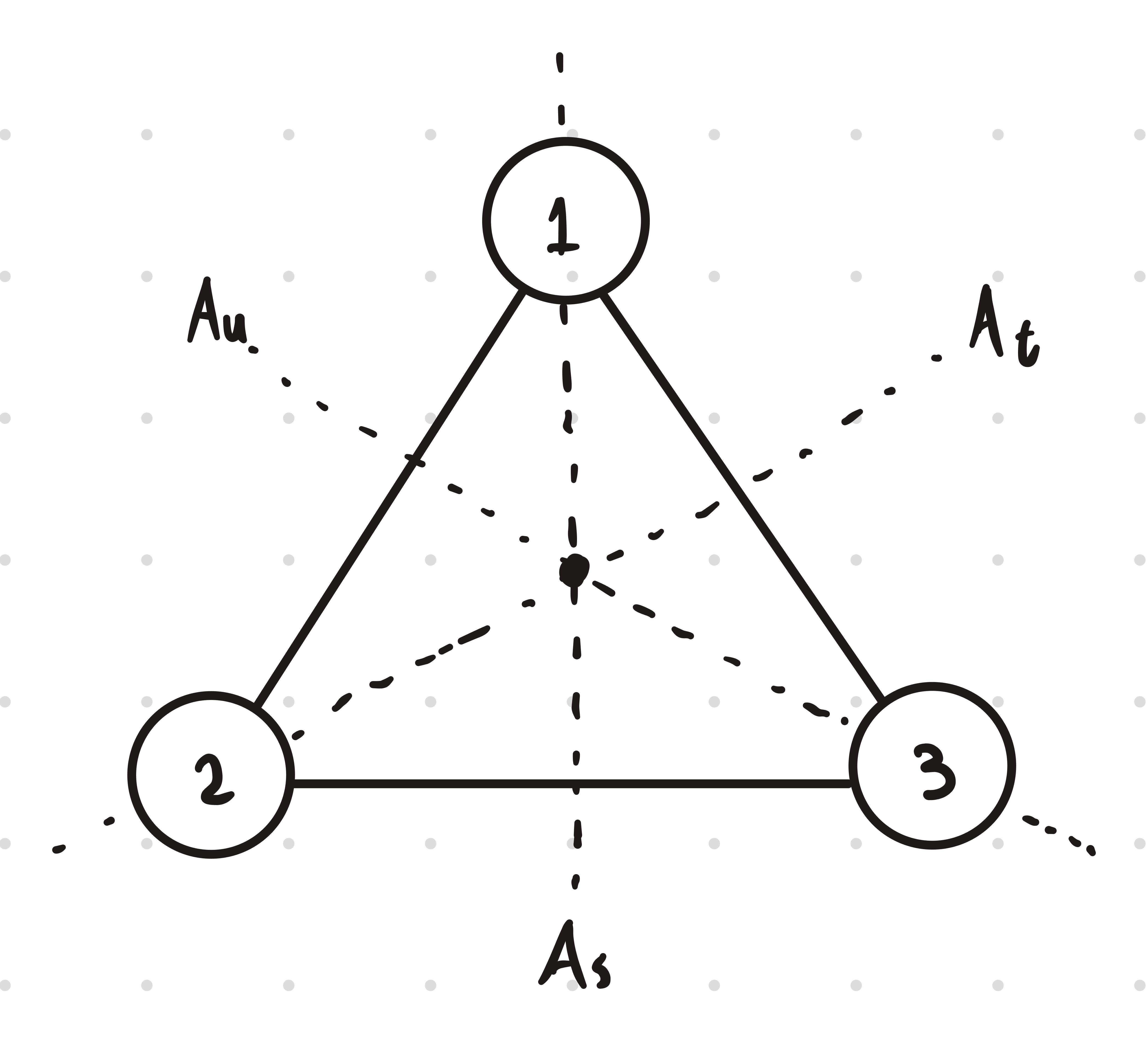
Node Positions
6 unique combinations
Transformation Representation
We can now write all transformations in terms of and
Satisfies Composition Rules?
Closure
For any the product
Associativity
For all elements in ,
Identity
There exists an element such that for every
Inverse
For each , there exists an element such that
Summary
- () is the dihedral group of order 6
- It captures all rotations and reflections of an equilateral triangle
- Every group axiom is satisfied, making it a proper mathematical group